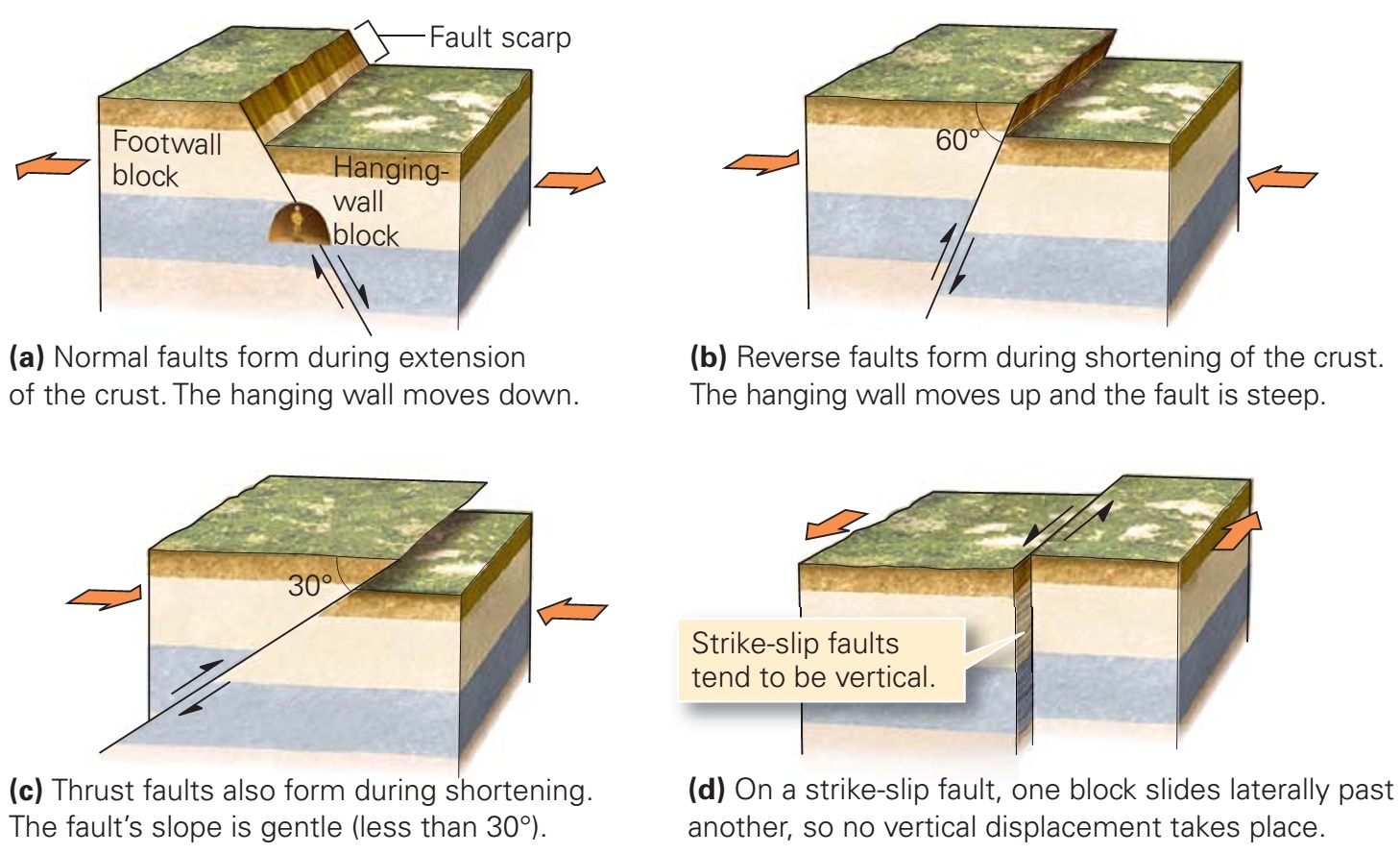
Define Shearing Geology . Shear zones, like faults, typically. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,.
from geologylearn.blogspot.com
shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. Shear zones, like faults, typically. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent.
Learning Geology What Causes Earthquakes?
Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. Shear zones, like faults, typically. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,.
From opentextbc.ca
15.1 Factors That Control Slope Stability Physical Geology 2nd Edition Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements. Define Shearing Geology.
From geologylearn.blogspot.com
Learning Geology Fault Terminology Define Shearing Geology Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. It is most. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 10 The Movement of the Earth’s Crust PowerPoint Define Shearing Geology It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other.. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.animalia-life.club
Folding And Tilting Of Rock Define Shearing Geology Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. Shear zones, like faults, typically. shear. Define Shearing Geology.
From hamed-geo.com
Types of Faults in Geology HamedGeo Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.researchgate.net
Pure shear rift model (left side) and simple shear rift model (right Define Shearing Geology Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones, like faults, typically. in. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.geoengineer.org
VertekCPT Do you know about Soil Shear Strength ? Define Shearing Geology shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically. Shear zones are. Define Shearing Geology.
From geologylearn.blogspot.com
Learning Geology Fault anatomy Define Shearing Geology a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones, like faults, typically. in. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT How do geologic processes change the shape of Earth’s surface Define Shearing Geology in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically. It is most often caused. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.mdpi.com
Geosciences Free FullText Constraining the Timing of Evolution of Define Shearing Geology in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. shear zones. Define Shearing Geology.
From www.anyrgb.com
Diagenesis, shear Zone, Foliation, Stratigraphy, rock Cycle Define Shearing Geology Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones, like faults, typically. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. in the world of geology, the term. Define Shearing Geology.
From schematicviciosinfin17.z22.web.core.windows.net
Normal Fault And Reverse Fault Diagram Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral. Define Shearing Geology.
From deeajtsneco.blob.core.windows.net
Shearing Meaning Geology at Tim Bartholomew blog Define Shearing Geology in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones, like faults, typically. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older. Define Shearing Geology.
From geologyscience.com
Stress and Strain » Geology Science Define Shearing Geology a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. Shear zones, like faults, typically. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. shear zones are zones of intense ductile. Define Shearing Geology.
From paleolimbot.github.io
Chapter 13 Geological Structures and Mountain Building Physical Geology Define Shearing Geology a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other. Shear zones, like. Define Shearing Geology.
From deeajtsneco.blob.core.windows.net
Shearing Meaning Geology at Tim Bartholomew blog Define Shearing Geology Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear. Define Shearing Geology.
From rogermarjoribanks.info
The Movement of Faults « Roger Marjoribanks Roger Marjoribanks Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. shear zones are zones of intense ductile deformation that are thin relative their lateral extent. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. in the world of geology, the term “shearing” describes. Define Shearing Geology.
From deeajtsneco.blob.core.windows.net
Shearing Meaning Geology at Tim Bartholomew blog Define Shearing Geology Shear zones, like faults, typically. a shear zone is the ductile, deep equivalent of a fault zone. It is most often caused by intense pressure under the. Shear zones are generally wider than faults and may accommodate displacements over a range. Shear zones, like faults, typically show offsets of older structures,. shear zones are zones of intense ductile. Define Shearing Geology.